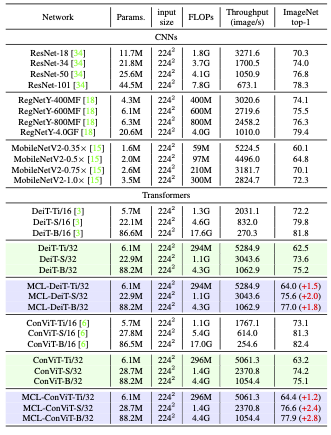
Recently, visual Transformers have showed great potential on various computer vision tasks. However, the large computational complexity might limit their applications on devices with constrained computing resources. Designing an efficient Transformer suitable for visual tasks is an urgent problem to be solved. Previous works showed that a larger patch size can significantly decreases the computational cost, as the number of patch embedding is decreased, but a larger patch size also leads to decreased final performance. Therefore, we propose a Multi-scale Cooperative Learning (MCL) framework to train an efficient visual Transformer. With the help of the proposed patch compression mechanism, MCL trains the visual Transformer model with smaller and larger patches simultaneously. Besides, a decompression module is introduced to relieve information loss during patch compression. After training, the embedding and compression modules are re-parameterized into a unified operation with for efficient inference with only the large patch size. Experiments on different visual Transformer architectures show the effectiveness and generalization ability of our MCL approach. For example, on ImageNet dataset, our MCL-DeiT-S/32 outperforms DeiT-Ti/16 by 3.4% with 1.5x faster inference speed. It also outperforms MobileNetV2-1.0$\times$ and RegNetY-400MF by 3.3% and 1.5% respectively while being faster than both of them.
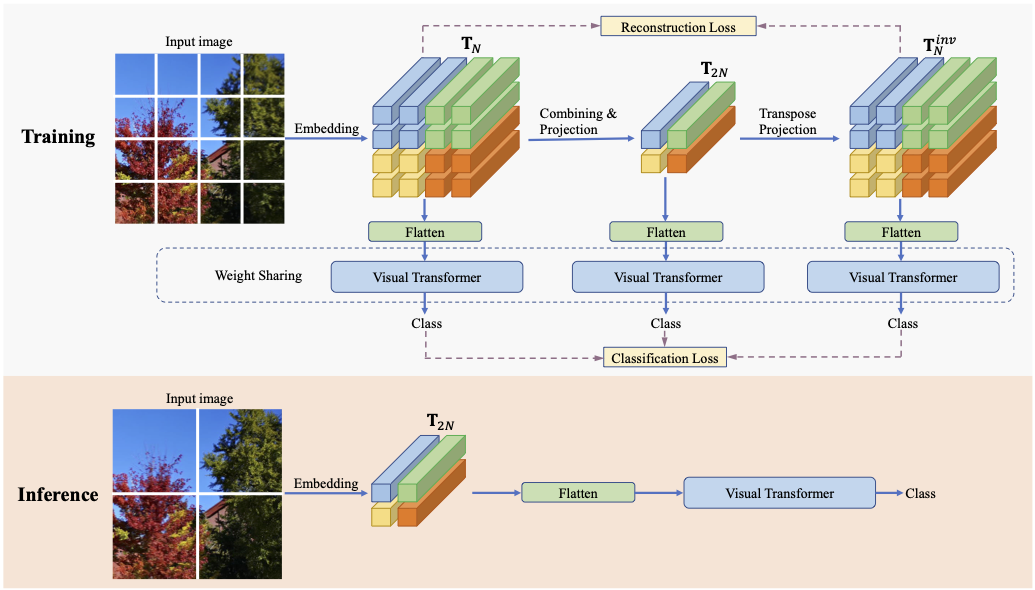
Illustration of the proposed Multi-scale Cooperative Learning framework. (Top) The training phase. The input image is transformed into patch embeddings of the small patch size, then combined and projected into fewer patch embeddings corresponding to larger patches. A transposed projection module is adopted to reconstruct the initial patch embeddings. All the patch embeddings are fed into the visual Transformer for joint learning. (Lower) The inference phase. Only the patch embedding generated by the largest patch size is used for efficient inference.
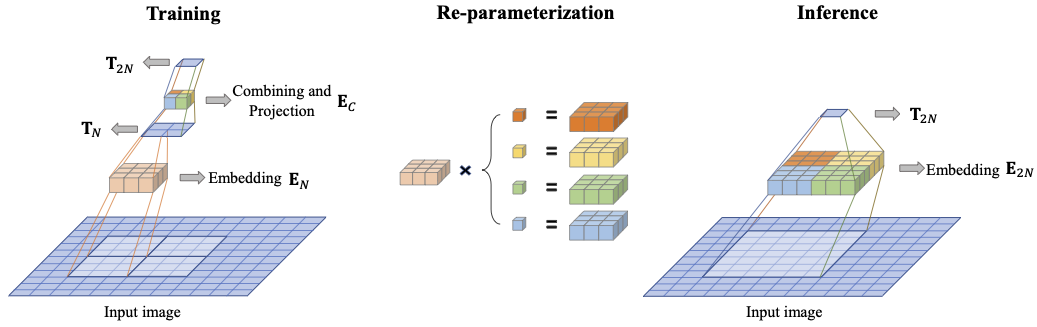
The combining and projection module is only used during training. When used for inference, the two projection matrices can be merged into a single one via re-parameterization as both projections are linear operations.